When it comes to electromechanical linear actuators, integrated designs offer space savings, reduced complexity, and lower total cost of ownership with fewer parts required for repair or replacement. One such design that’s found multiple uses in medical, 3D printing, and assembly applications is the hybrid stepper motor linear actuator, which combines a ball or lead […]
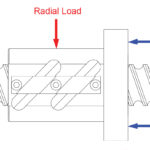
How axial and radial loads affect linear motion systems
In any motion system, understanding the type and direction of applied and resultant loads is important for determining bearing life and analyzing deflection. In linear motion systems, we typically use Cartesian coordinates (X, Y, and Z) to define the placement and direction of loads. But for rotating components such as screws, rack and pinion drives, […]
Piezo motors vs. voice coil actuators for micron and sub-micron positioning
Applications that require micron or sub-micron level positioning with extremely smooth motion and control often call for a direct drive system — linear motor, piezo motor, or voice coil actuator. Linear motor stages are typically used when high forces are needed over stroke lengths greater than a few hundred millimeters. But for high-precision applications with […]
How to account for rack and pinion inertia during system design
Rack and pinion drives are often used in applications that require stroke lengths beyond the practical limits of ball screws and thrust forces that exceed the capabilities of belt drives. And in some applications, rack and pinion systems can also provide lower total inertia than a suitable ball screw or belt drive alternative, which can […]
Linear motion basics: 13 fundamental topics you need to know
Whether you’re new to designing and sizing linear motion systems, or you could just use a refresher, we’ve gathered all the articles that cover mechanical concepts used in linear motion systems and put them together here, as a sort of “linear motion basics” reference guide. Unlike our curated lists of articles that address sizing and […]
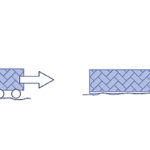
What factors contribute to friction in linear motion systems?
Designers and engineers typically try to avoid or mitigate friction in linear motion systems. Although friction isn’t always bad — in some applications, it can provide a damping effect and help improve servo tuning — when it comes to linear motion systems, it increases the amount of force required to move a load, creates heat, […]
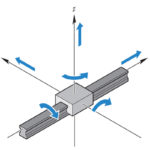
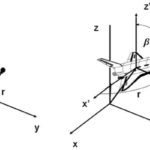
Degrees of freedom (DOF) basics for motion engineering
To identify the position of an object in three-dimensional space, we use a coordinate system that defines three axes: X, Y, and Z. If the object is a point mass, we only need three coordinates (X, Y, and Z) to locate its position. But a rigid body can both move, or translate, along these three […]
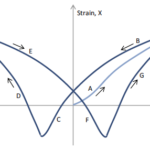
How does hysteresis affect piezo actuator performance?
Piezo actuators operate on the principle that application of an electric field (voltage) induces strain (displacement) in the material — a phenomenon known as the inverse piezoelectric effect. But if you plot the strain versus the electric field of a piezo material, you’ll see that the strain doesn’t follow the same path when the field […]
Single-axis linear stepper stages with integrated encoder and electronics package
H2W now offers a revolutionary series of single-axis linear stepper stages that integrates a linear encoder into the stage to operate the linear stepper motor as a 2-phase brushless motor when coupled with an advanced motion control electronics package provided by H2W. When operated this way, the motors will tend to run cooler, as they […]
What makes a linear stage different from other types of linear motion systems?
Linear motion systems — consisting of a base or housing, a guide system, and a driving mechanism — are available in a wide variety of designs and configurations to suit almost any application. And because their designs are so varied, they’re often categorized according to key construction and operating principles. Case in point: The term […]