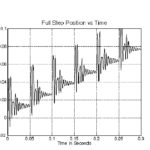
The discrete, step-by-step movements that give a stepper motor its accurate positioning capability can also lead to some undesirable performance characteristics — namely, vibration and audible noise due to resonance. Stepper motors naturally exhibit small vibrations with each step, due to the inertia of the moving rotor, which causes the motor to slightly overshoot (or, […]
Controls for linear axes
Nanopositioning controller for piezo stages boasts 270-W peak power, nanometer-level precision
A high-power version of PI’s (Physik Instrumente) E-727 family of multi-axis piezo nanopositioning controllers provides 270 W of peak power – close to 10X of the standard version. The enhanced performance is useful for dynamic, nanometer-level precision motion and positioning applications, such as FSM (fast steering mirrors) in free space optical communication and laser material […]
Linear servo brush-type amplifiers for voice-coil actuators
H2W’s new dc linear brush-type servo amplifier, the LCAM 5/15, is suited to drive the company’s line of voice coil linear actuators. Linear amplifiers provide continuous current flow to the motor which prevents any dead-band issues that occur in many PWM type amplifiers. Additionally, linear amplifiers have low EMI, and no audible noise that also […]
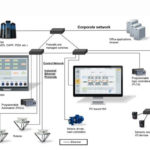
Industrial Ethernet basics for mechanical engineers
Ethernet networks are ubiquitous in our daily lives — allowing computers in office, school, and commercial environments to connect to the internet, share files, and access printers and other hardware connected to the network. And there’s a reason Ethernet is so popular — it’s a simple, flexible network protocol that facilitates high-speed data transmission. But despite […]
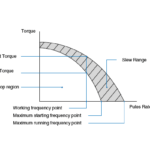
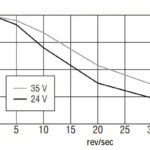
Stepper motor torque and speed characteristics explained
Stepper motors have different torque-speed characteristics depending on whether the motor is starting/stopping or already running. These characteristics are depicted in two curves on the motor’s torque-speed chart, and it’s important to understand the differences between these curves and what each one means for the motor’s operation. But a stepper motor can also produce torque […]
Boosting productivity with the right direct-drive motor and linear-motor feedback
Feedback options for linear motors and direct-drive torque motors abound. The most common employ optical, magnetic, capacitive, or inductive measurement. Here we explain how the key application parameters of precision, cost restrictions, and insensitivity to mechanical characteristics and environment dictate which technology is most suitable. By Steffen Preg | CEO • SIKO Products Inc. Machines […]
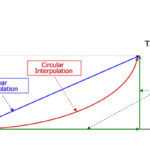
What types of motion can you create with multi-axis linear systems?
For many tasks, multi-axis linear systems — Cartesian robots, X-Y tables, and gantry systems — travel in straight lines to achieve quick point-to-point movements. But some applications, such as dispensing and cutting, require the system to follow a circular path or a complex shape that can’t be created by simple lines and arcs. Fortunately, modern […]
Stepper motor performance: Is it possible to get high torque at high speeds?
The most notable stepper motor performance characteristics are precise positioning, good holding torque, and good low-speed torque characteristics. But in some cases, application parameters necessitate high torque production at high speeds, while design or control constraints dictate the use of a stepper motor. Although stepper motors aren’t notable for their ability to produce high torque […]
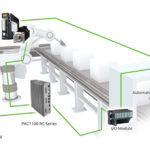
Motion controller basics: What are the differences between PLCs, PACs, and IPCs?
As the “brain” of a servo system, a motion controller is responsible for ensuring the motor is following the specified motion profile and correcting any errors between the commanded value (in terms of position, speed, or torque) and the motor’s actual value. The motion controller also handles other supervisory and processing tasks, such as ensuring […]
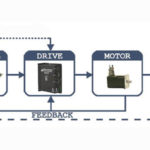
What’s the difference between a servo drive and a motion controller?
Servo systems are made up of four key parts: a motor, a feedback device, a servo drive, and a motion controller. The servo drive and motion controller work together (supported by information from the feedback device) to provide the correct power to the motor so that it executes the intended movement or produces the desired […]