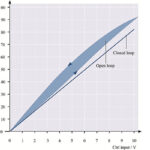
Piezo actuators exhibit a linear* relationship between applied voltage and displacement, responding almost instantly to any change in voltage. But they also experience creep — a phenomenon in which the actuator continues to expand or contract even after the voltage change is complete. Piezo actuator creep Creep occurs because piezoelectric materials have an asymmetric charge […]
Mini + piezo + voice coil
Open aperture voice coil stages with 1.20 inch travel and 25.4 micron resolution
Moticont’s HCDS-051-064 series of open aperture voice coil stages are linear DC motor driven stages. Designed for closed loop servo operation, an integral quadrature optical encoder with differential outputs is standard. The stages are clean, quiet, and efficient, with low inertia, high acceleration, and high speed. Each stage has a built-in home switch for accurate […]
Piezo motors vs. voice coil actuators for micron and sub-micron positioning
Applications that require micron or sub-micron level positioning with extremely smooth motion and control often call for a direct drive system — linear motor, piezo motor, or voice coil actuator. Linear motor stages are typically used when high forces are needed over stroke lengths greater than a few hundred millimeters. But for high-precision applications with […]
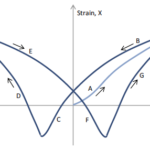
How does hysteresis affect piezo actuator performance?
Piezo actuators operate on the principle that application of an electric field (voltage) induces strain (displacement) in the material — a phenomenon known as the inverse piezoelectric effect. But if you plot the strain versus the electric field of a piezo material, you’ll see that the strain doesn’t follow the same path when the field […]
Low inertia, high precision linear voice coil stages from Moticont
Moticont has introduced two high performance linear DC motor driven stages. The VCDS-051-032-01-B1-30 (pictured) and the VCDS-051-032-01-F1-30 linear voice coil stages feature high speed, high acceleration/deceleration, zero backlash, smooth motion, precise positioning of 30 microns, high reliability and low cost. These non-commutated stages are clean room friendly, quiet, and available off-the-shelf. With a 0.97 in. […]
Linear slide with maintenance-free voice coil motor features nanometer precision
PI extends its large offering of nanometer precise, fast focusing stages with the addition of its new V-308 nanopositioning slide for vertical applications providing 7 mm of Z-travel and 10 nm incremental motion, making it suitable for OEM and research applications in the life science, semiconductor, and material science fields. The novel design combines long […]
What’s the difference between a vertical lift stage and a Z axis actuator?
In many applications that require vertical motion, a Z axis actuator is combined with one or two horizontal axes in a Cartesian or gantry-style arrangement. In these multi-axis configurations, the moved load is mounted to the Z axis via a bracket, creating a moment load that affects not only the Z axis, but also the horizontal […]
What’s the difference between minimum incremental motion (MIM) and resolution?
When we talk about the positioning capabilities of a linear motion system, we typically talk about accuracy and repeatability, and in some applications — especially those driven by stepper motors — we may also be concerned with resolution. But accuracy and repeatability define a system’s ability to reach its commanded position and to do so over […]
Hexapods precisely jostle cameras during image-stabilization testing
The six-axis parallel-kinematics systems known as hexapods excel in motion simulation and testing of mechanical and drive systems, multi-dimensional position sensors, and (the focus of this article) image-stabilization designs for cameras and video equipment. By Doris Knauer • Project Manager — Industrial Automation | Physik Instrumente (PI) Modern camera systems are capable of astounding feats, […]
Linear motion in medical applications: Piezo actuators for non-contact dispensing
In a recent article, we looked at how piezo motors are used in liquid handling robots for contact-based dispensing (also referred to as pipetting) of microliter and nanoliter volumes. But when the required dispense volumes fall in the single-digit nanoliter or picoliter range, the process often requires a non-contact dispensing method to ensure accuracy and […]