Although there are more than a dozen symptoms of premature wear and impending failure for V-belts — ranging from visible damage to audible noise — there are a few key ways that these friction-based belts can fail during operation. To help users determine the root cause of a failure or signs of potential failure, V-belt […]
Linear drives (all)
When are stepper motors paired with ball screws (rather than lead screws)?
Stepper motors are widely used in industrial and consumer applications ranging from packaging equipment and medical devices to 3D printers and vending machines. They have excellent torque production at (relatively) low speeds — especially for a given motor size — and offer high-resolution positioning in a simple-to-use format. These benefits make them well-suited to drive lead […]
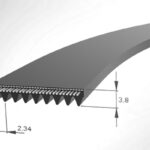
What do the belt section designations H, J, K, L, and M mean for ribbed V-belts?
V-belts rely on friction caused by the “wedging” of the belt between pulley flanges — together with internal fiber cords — to transmit power in a wide range of industrial and consumer-goods applications. One variation of the traditional V-belt is the ribbed V-belt — also referred to as a V-ribbed, poly V, or serpentine belt. Ribbed V-belts take […]
Causes of tooth shear in synchronous belts, and how to avoid it
Synchronous belts transmit power via positive engagement between belt teeth and pulley grooves, making them suitable for applications that require high torque and making them less prone than traditional V-belts to slip in dynamic applications. But even synchronous belts can experience failure if they’re not installed, maintained, and applied properly. One way that toothed belts […]
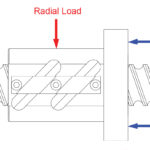
How axial and radial loads affect linear motion systems
In any motion system, understanding the type and direction of applied and resultant loads is important for determining bearing life and analyzing deflection. In linear motion systems, we typically use Cartesian coordinates (X, Y, and Z) to define the placement and direction of loads. But for rotating components such as screws, rack and pinion drives, […]
How to account for rack and pinion inertia during system design
Rack and pinion drives are often used in applications that require stroke lengths beyond the practical limits of ball screws and thrust forces that exceed the capabilities of belt drives. And in some applications, rack and pinion systems can also provide lower total inertia than a suitable ball screw or belt drive alternative, which can […]
How to account for belt and pulley inertia during system design
In order for a motor to accelerate or decelerate a load, it must overcome the load’s inertia, or resistance to change in motion, as explained in Newton’s First Law. In belt-driven linear motion systems, the motor has to overcome not only the inertia of the applied load, but also the inertia of the belt, pulleys, […]
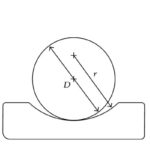
Motion basics: What is ball conformity in linear guides and screws?
In linear guides and ball screws, load-carrying balls or rollers can ride on planar (flat) raceways, as with non-recirculating linear roller bearings, or in curved raceways, as with ball screws and profiled rail guides. When a ball or roller rides on a planar raceway, the contact between the rolling element and the raceway will be […]
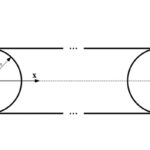
Motion basics: What is differential slip and how does it affect linear bearings?
Linear bearings that use balls or rollers are typically chosen for their ability to carry high loads with very low friction. But rolling elements — including linear bearings — are not friction-free. One of the factors that contributes to friction in linear bearings (along with properties such as surface roughness, elastic hysteresis of the materials, and […]
What’s the difference between ANSI and ISO ball screw load capacity?
The dynamic load capacity of a ball screw is typically defined by the DIN ISO 3408-5 standard, or in some cases, by the JIS B1192-1997 standard, both of which use 1 million revolutions as the basis for load capacity. However, some manufacturers determine ball screw dynamic load capacity according to the ANSI ASME B5.48-1977 standard (reconfirmed […]