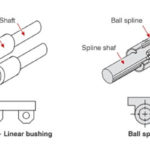
Linear ball bushings are one of the few interchangeable product types in linear motion, with industry-standard sizes and styles, so that a product from one manufacturer can often be substituted with a product from another manufacturer that has very similar dimensions and technical specifications. And most linear bushing manufacturers offer several product lines that are dimensionally the same but have functional or performance differences. This means that if an application’s requirements change or a product becomes unavailable, a nearly identical replacement bushing is typically easy to find.


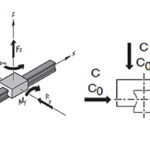
1) unloaded balls
2) load-bearing balls
Image credit: Bosch Rexroth
Type and dimensions
The first step in the interchange process for linear bushings is to identify the type of bearing and its basic size. “Type” generally refers to whether the bearing is closed, for use on an unsupported shaft, or open, for use on a supported shaft. If the bearing is adjustable — meaning its diameter can be adjusted to reduce play or create preload — that should also be considered when determining the bearing type. The bearing size refers to the diameter of the shaft on which the bearing rides (0.5 in. or 12 mm, for example).
Although most linear bushing interchange tools base their selections only on bearing type and shaft diameter, the overall length and outer diameter of the bushing are important as well, especially in the case of an interchange, where the bushing is typically being mounted in an existing housing or framework. Depending on the number of ball circuits and the type of ball recirculation (tangential or radial), the outer diameter and overall length of the bushing can vary significantly, even for the same basic size (shaft diameter).
If the bushing is mounted in a manufacturer-supplied housing, or pillow block, be sure to check the width and height of the pillow block as well as the distance from the base to the center of the shaft.

Seals and wipers
The next thing to consider is sealing. Does the bearing have seals on both sides, on one side only, or is it unsealed? Specifying the type of sealing is not only important for contamination protection, but also because seals add friction, which requires more force to move the bearing. External seals or wipers (which are often sold as separate parts, but can sometimes be specified in the bushing part number) can also add length to the bearing, which is especially important to consider if the bearing is mounted in an existing housing or fixture.
Load capacity
To ensure that an interchange for an existing linear bushing is functionally the same, it’s important to compare the load capacities of the old and new selections. Like overall dimensions, a bushing’s load capacity is determined, in part, by the number of ball circuits and the type of ball recirculation. Even if all dimensions are the same or very similar, linear bushings of the same size can have significantly different load capacities. It’s also important to remember that some ball bushings are rated for 50,000 m life, while others are rated for 100,000 m, so it may be necessary to apply a correction factor to the dynamic load capacity of one bushing in order to make a true comparison with another product.
To complete your linear bushing assembly, check out these tips on selecting shafts for linear bearings.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.