Dave Barta
Christian Stefanovitz
MPE Inc.
Carts that carry ultrasound and other medical devices must be sturdy and have shelves that are easily raised and lowered without binding. Dual vertical linear guides are commonly used, however, when the guides are not precisely parallel, they bind.
Recently, MPE, Inc., Milwaukee, Wisconsin, a contract manufacturer of custom carts and assemblies for medical and electronic OEM’s, used UtiliTrak linear guides made by Bishop-Wisecarver for directing the vertical motion of a shelf on a cart specifically intended to hold a Siemens portable ultrasound device. The guide system contains a carriage equipped with double-V wheels that move along an inverted V- channel. The standard carriage has three inline wheels that have a constant radius ball bearing path to minimize vibration, move smoothly, and double-row bearings to minimize friction.
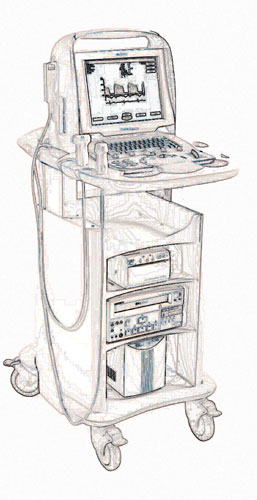
A custom
UtiliTrak carriage with five wheels makes the Siemens cart extremely
stable and easy to guide. The fifth wheel increases the load capacity
needed for vertical motion.
Sizing and selecting a wheel carriage assembly includes three steps:
1. Determine Radial and Axial Loads
A radial load is applied perpendicular to the bearing shaft, while an axial load is applied parallel to the bearing shaft. The axial load on a guide-wheel is a moment load, because it affects only one side. Since the ball bearing elements are not equally loaded, one side of the wheel is free, while the other side interacts with the track. To offset the moment load, the radial preload is increased, supporting higher axial loads.
2. Calculate Load Factors
All statics calculations must be considered, including inertial forces, gravitational forces, external forces, bearing element spacing, payload magnitude, and travel direction. In this application, because movements are vertical, gravity is an essential consideration. Moreover, any external forces that generate a reaction through the wheel-track interface must be considered.
3. Apply Safety Factors
A derating factor applies to the maximum axial and radial working load capacities because load, speed, shock, vibration, contamination, and duty cycle requirements may vary. De-rating factors found in the manufacturer’s literature can be used.
A pair of gas springs was used as actuators, and connected to the top shelf casting to counterbalance the weight of the ultrasound device. This allows the top to be raised and lowered with little effort. The guide-way preload is factory adjusted, using eccentric and concentric studs.
www.bwc.com
:: Design World ::


good site thanks for sharing