Ultrasonic piezo motors create useful rotary or linear motion by exciting a piezo element to produce high-frequency oscillations. In linear ultrasonic piezo motors, the piezo element is a piezoelectric plate. Applying voltage excites the plate at its resonance frequency and creates eigenmode oscillations – meaning all parts of the plate move sinusoidally at the same frequency. The piezoelectric plate is preloaded against a runner (also referred to as a “slider”) via a coupling, or pusher. Oscillations in the plate cause it to expand and contract, moving the coupling along an inclined patch. The coupling, in turn, makes contact with the runner and causes it to move linearly.

Image credit: Physik Instrumente GmbH
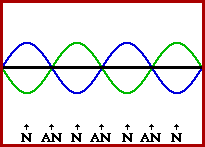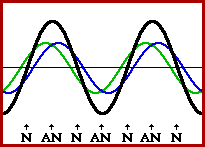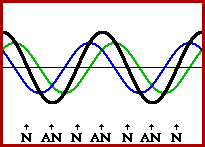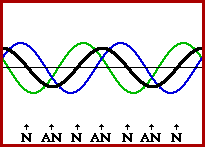
Image credit: The Physics Classroom
Ultrasonic piezo motors are sometimes referred to as “standing wave piezo motors,” due to the type of wave generated when the piezoelectric material is excited. A standing wave is formed when an incident (original) wave and a reflected wave interfere in such a way that there are points along the medium that appear to be standing still. Hence, the name, “standing wave.”
Although linear ultrasonic piezo motors are capable of unlimited travel, the length of the runner determines the actual stroke, with maximum travel capabilities of 100 to 150 mm. Linear ultrasonic designs have low inertia with fast response times and are capable of achieving velocities up to 1 m/s and accelerations of 10 to 20 g. On the other hand, they’re also capable of ultra-slow motion, down to just a few nanometers per second. Because they rely on friction between the coupling and the runner, resolution is somewhat limited (relative to other piezo motor designs) to between 50 and 80 nm. But this friction allows ultrasonic piezo motors to be self-clamping in a power-off condition, capable of producing 2 to 3 N of holding force without heat generation.
Linear ultrasonic piezo motors are most commonly used in metrology and scanning equipment. Because they’re vacuum-compatible and contain no magnetic components, they’re well-suited for use in military and aerospace applications, such as guidance systems and antenna positioning. Medical imaging devices often incorporate linear ultrasonic piezo motors for fine positioning of imaging equipment.
This video from PI shows how linear ultrasonic piezo motors create useful motion.






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.