In an ideal world, a linear motion system would exhibit perfectly flat, straight motion and reach the intended position with zero error every time. But even the highest precision linear guides and drives (screws, rack and pinions, belts, linear motors) have some errors due to machining tolerances, handling, mounting, and even the manner in which they’re applied.
There are three types of errors found in linear motion systems — linear errors, angular errors, and planar errors — and each type has a different effect on the system and the application. To avoid paying for high-precision components where they’re not needed, or ending up with a system that doesn’t meet the application requirements, it’s important to understand the differences between these three types of linear motion errors and their causes.
Linear errors
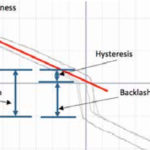
Linear errors include positioning accuracy and repeatability. These errors are sometimes referred to as positioning errors because they specify the system’s ability to reach the desired position. In the context of linear systems, the term “accuracy” typically refers to positioning accuracy, which is the deviation between the target position and the position the system achieved. Repeatability refers to how well a system returns to the same position over multiple attempts. The main contributor to linear errors is the drive mechanism (screw, rack and pinion, or linear motor, for example), but the system’s tuning can also affect its ability to reach the target position accurately and repeatably.
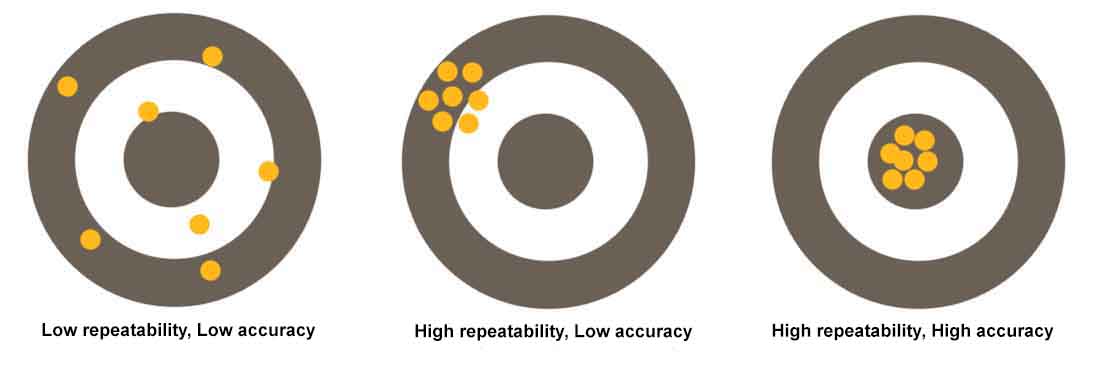
Image credit: Parker Hannifin
Angular errors
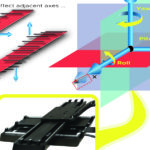
Angular errors are errors in which the point of interest rotates around an axis. These are typically referred to as roll, pitch, and yaw errors, denoting rotation around the X, Y, or Z axis, respectively. If the point of interest is the center of the table, or slide, angular errors may not have a significant effect on the application. But when the point of interest is some distance away from the table or slide, Abbé errors, which are angular errors amplified by distance, can produce undesirable results, especially in machining, measuring, and assembly applications. The primary causes of angular errors, and by extension, Abbé errors, are inaccuracies in the linear guides and poorly machined mounting surfaces.
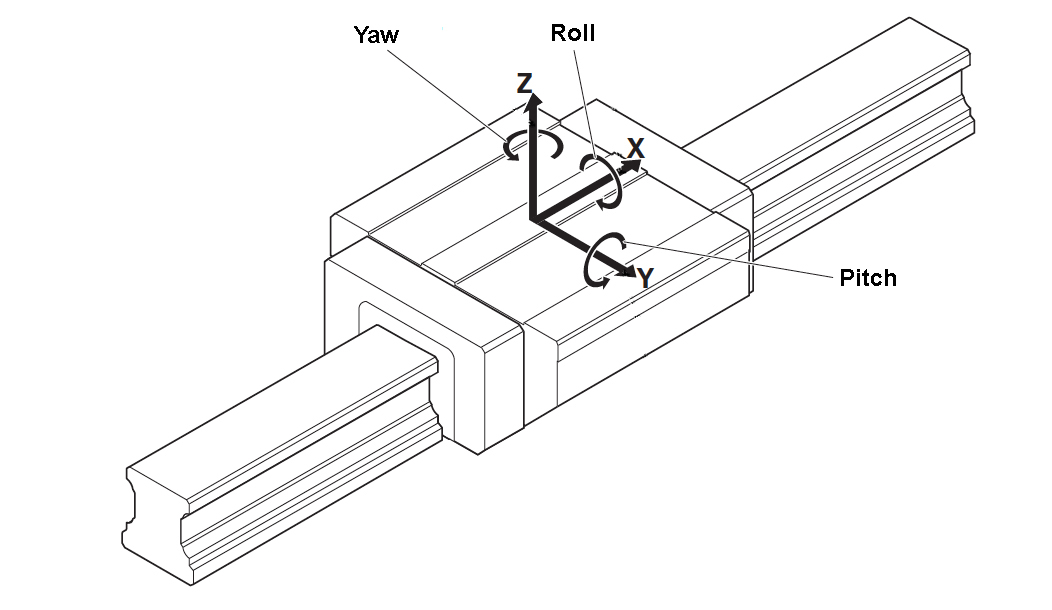
Image credit: Bosch Rexroth Corp.
Planar errors
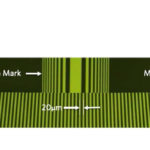
Planar errors — often referred to as “straightness” and “flatness” — occur during the system’s travel, but rather than rotation around an axis, planar errors are deviations from an ideal, straight reference plane. Straightness defines the extent of motion along the Y axis as the system travels along the X axis. Similarly, flatness defines the extent of motion along the Z axis as the system travels along the X axis.
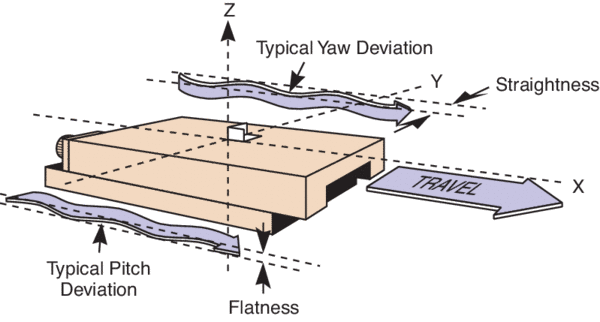
Image credit: Newport Corporation
Note here that the point of reference is the axis of travel (typically the X axis), so there are only two types of planar errors, involving motion along the remaining two axes.
Planar errors are detrimental to applications such as dispensing, machining, or measuring, where the system’s behavior during motion is critical. In multi-axis systems, planar errors in one axis affect the adjacent axis (or axes), especially when the axes are “stacked,” such as in X-Y tables, planar tables, and some Cartesian systems.



Such an insightful post. Keeping note for your records is important. Thanks for sharing. 🙂