Voice coil actuators are a type of direct drive mechanism that provides extremely precise positioning over small displacements. Like linear motors, they work on the principle of a permanent magnet field and a coil winding. When a current is applied to the coil, a force is generated. This force, known as the Lorentz force, is determined by the product of the current and the magnetic flux, and is given by:
F = k*B*L*I*N
Where:
F = force (N)
k = force constant
B = magnetic flux density (tesla)
L = length of wire (m)
I = current (amps)
N = number of conductors
For a given voice coil, all parameters are fixed except the current. Therefore, the force generated is directly proportional to the input current. The direction of the force is perpendicular to both the direction of magnetic flux and the direction of current. Changing the direction of the current changes the direction of the force.
The term “voice coil” comes from one of the first applications: vibrating the paper cone of a loudspeaker. In recent years, the most common application for voice coils has been to move the heads inside computer disk drives, but they’re also widely found in medical devices, mirror controls, and oscillating systems.
Operationally, the force produced by a voice coil causes the moving part to travel, which in turn pushes or pulls the load in a straight line. The moving part can be either the coil or the magnet, with the advantage of a moving coil being that it has a much lower mass than the magnet assembly. On the other hand, the coil generates heat, so if the load is sensitive to temperature fluctuations, attaching it to a moving magnet may be a better option.

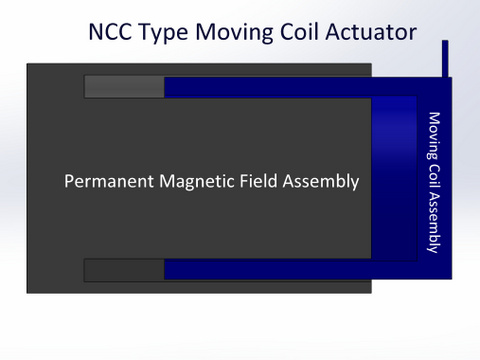
Voice coils are suitable for fixed-stroke applications, with typical maximum strokes of 5 to 6 inches. The force generated is fairly constant throughout the stroke length, with a small dropoff, typically less than 5 percent, at the ends of stroke.
The direct drive nature of voice coils means they have no backlash and can achieve high acceleration and deceleration rates. On the other hand, they also work well in applications with extremely slow speed and low acceleration/deceleration.
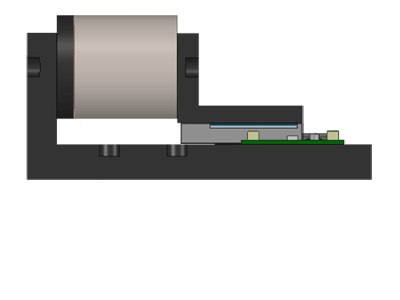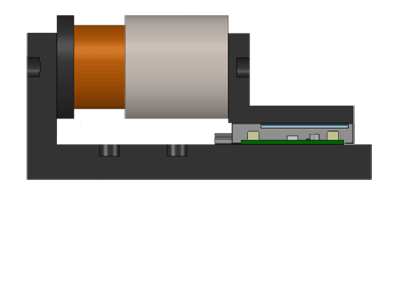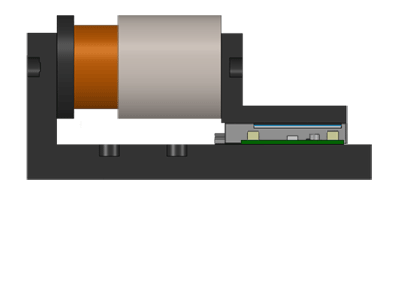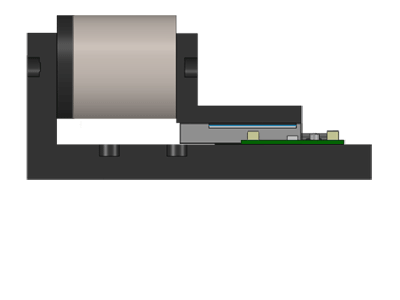
Image credit: Moticont
For a complete actuator, a voice coil is paired with linear bearings for guidance—typically air bearings or crossed roller guides, although linear shafts and round bearings are also suitable since they have very low friction. A feedback device and servo controller provide a closed-loop system for extremely precise position and velocity control. Even without a feedback device, a voice coil actuator has good force control due to the fact that the force generated is directly proportional to the applied current.
Voice coils draw current when holding a load in a fixed position, or in vertical applications when counteracting the weight of the load. In addition, when the coil moves rapidly, a back EMF is generated, which is proportional to speed, current, and magnetic field strength. This back EMF reduces the voltage across the coil, which reduces the current and limits acceleration.
To see how simple the integration and setup of a voice coil actuator can be, check out Design World’s review of the VCA Developer’s Kit from BEI Kimco.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.