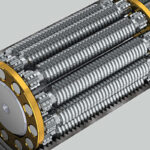
Ball and lead screws are specified by the diameter of the screw shaft and the lead (or, in some cases, pitch) of the screw thread. The lead, which specifies how far the nut travels for each revolution of the screw, is created by the thread, or helix, that wraps around the screw shaft. If the […]
FAQs + basics
How to calculate duty cycle and what it means for machine life
Determining the life of a linear system that uses balls or rollers is relatively straightforward, thanks to the L10 bearing life equation, which gives life in meters of travel (for linear bearings) or revolutions (for screws). And for plain bearings and lead screws, manufacturers typically use the bearing’s PV value and operating conditions to provide an […]
Comparing micropositioning and nanopositioning stages
Linear stage designs can range from long-stroke, high-load gantries to micropositioning and nanopositioning stages with light payloads. Although all linear stages are designed and constructed to provide high positioning accuracy and repeatability and to minimize angular and planar errors, stages for micropositioning and nanopositioning applications require additional considerations in component selection and design to achieve these […]
What is an inverted roller screw and how does it work?
Roller screws are often thought of as the standard planetary design, but several variations exist, including differential, recirculating, and inverted versions. Each design offers unique benefits in performance capabilities — load capacity, torque, and positioning — but the inverted roller screw’s primary strength is its ability to be easily integrated into actuators and other subassemblies. Recall that […]
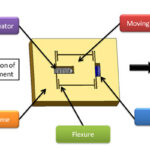
What are piezo flexure stages and how do they work?
Piezo actuators provide highly responsive, rapid movements, but their displacement is limited to just 0.1 to 0.2 percent of the actuator length. To overcome this limited stroke capability, a piezo actuator can be combined with elements, such as flexures, that provide mechanical amplification. The amplification provided by a flexure mechanism can extend the stroke of […]
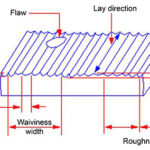
Linear bearing basics: Surface roughness, texture, and finish
One of the factors to consider when selecting shafts for linear bearings is surface roughness, which describes the microscopic asperities, or peaks, and valleys present on a material’s surface. But surface roughness is an important specification for all types of linear guides and screws — whether plain or recirculating, round shaft or profiled rail, ball […]
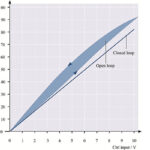
What are piezo actuator creep and drift?
Piezo actuators exhibit a linear* relationship between applied voltage and displacement, responding almost instantly to any change in voltage. But they also experience creep — a phenomenon in which the actuator continues to expand or contract even after the voltage change is complete. Piezo actuator creep Creep occurs because piezoelectric materials have an asymmetric charge […]
Screw handedness: When do you need a left-handed screw?
Just like people, ball and lead screws can be either right-handed or left-handed. But in screw terminology, handedness indicates the direction in which the nut moves relative to the direction of the screw’s rotation. By far the most common version is the right-handed screw, in which the nut moves toward you when the screw is […]
What is torque ripple and how does it affect linear motion applications?
Motors produce torque and rotation through the interaction of magnetic fields in the rotor and the stator. In an ideal motor — with mechanical components that are perfectly machined and assembled and electrical fields that build and decay instantaneously — torque output would be perfectly smooth, with no variations. But in the real world, there […]
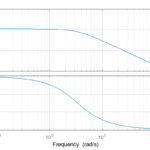
What does bandwidth refer to in the context of servo systems?
Most people are familiar with bandwidth as it relates to networking and WiFi service — for example, the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands on which WiFi signals are transmitted. But bandwidth also plays an important role in servo control and tuning. The bandwidth of a servo control system indicates how quickly the system […]