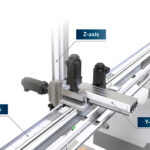
Cartesian robots with the right design upgrades can assume manual transfer operations. By Michael Everman • Founder and CTO | Bell-Everman Manufacturing and packaging operations using manual material or parts handling operations can reap immediate benefits from automation with long-travel Cartesian robots having custom end-of-arm tooling (EoAT) and advanced sensing capabilities. These robots can support […]
Belt + chain drives for linear
Mobile version of Gates Design Power now available
Gates just released a mobile version of Gates Design Power — a digital design tool to support the engineering of belt drive systems on customers’ mobile devices. “With the launch of Design Power Mobile, we’re demonstrating our ongoing commitment to accelerate our Chain to Belt initiative, driving the conversion of legacy drive technologies to clean, […]
Update on today’s belt drives
Belt drives have continued to evolve with new applications. Industrial belt drives in motion designs consist of rubber, engineered plastic, metal, or (most common) multi-material belts that wrap around drive pulleys — grooved or otherwise profiled wheels mounted on a shaft — in turn driven by electric motors. Powered by various motor types, belt drives run […]
igus offers custom toothed belt pulleys delivered in 48 hours
igus is expanding its 3D-print and online ordering offering to include custom format toothed belt pulleys. Toothed belt pulleys are a common component in many machines and are widely used in linear drives of printers, robots, and packaging machines. However, if an individual variant is required, developing a custom component can take days or even […]
Self-lubricating toothed belt axis for clean use in food manufacturing
igus has introduced a maintenance-free toothed belt axis specifically designed to improve sanitation in food manufacturing systems. The new drylin ZLW toothed belt axis is based on hygienic design principles and uses FDA-compliant materials. Cleaning complex machines and systems in food production leads to longer and therefore expensive downtime. For instance, industrial bakeries are faced […]
Troubleshooting V-belt wear and failure
Although there are more than a dozen symptoms of premature wear and impending failure for V-belts — ranging from visible damage to audible noise — there are a few key ways that these friction-based belts can fail during operation. To help users determine the root cause of a failure or signs of potential failure, V-belt […]
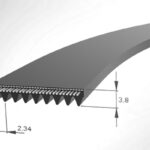
What do the belt section designations H, J, K, L, and M mean for ribbed V-belts?
V-belts rely on friction caused by the “wedging” of the belt between pulley flanges — together with internal fiber cords — to transmit power in a wide range of industrial and consumer-goods applications. One variation of the traditional V-belt is the ribbed V-belt — also referred to as a V-ribbed, poly V, or serpentine belt. Ribbed V-belts take […]
Causes of tooth shear in synchronous belts, and how to avoid it
Synchronous belts transmit power via positive engagement between belt teeth and pulley grooves, making them suitable for applications that require high torque and making them less prone than traditional V-belts to slip in dynamic applications. But even synchronous belts can experience failure if they’re not installed, maintained, and applied properly. One way that toothed belts […]
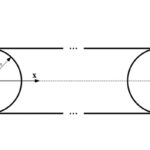
How to account for belt and pulley inertia during system design
In order for a motor to accelerate or decelerate a load, it must overcome the load’s inertia, or resistance to change in motion, as explained in Newton’s First Law. In belt-driven linear motion systems, the motor has to overcome not only the inertia of the applied load, but also the inertia of the belt, pulleys, […]
What are some linear motion options for moving multiple loads independently?
From a mechanical standpoint, one of the more challenging applications in linear motion has traditionally been to move two or more loads independently, as is required in some handling, transport, and inspection applications. While using multiple linear systems, or preassembled actuators, is a simple solution mechanically, this option typically requires a significant amount of space […]