Automation over the last several years has expanded use of electric linear actuators to leverage their technological advancements in smart homes, aerospace, defense, and industrial applications. In fact, the global linear actuator market could (in large part because of electric options) surpass U.S. $52.67B this year and grow at a compound annual growth rate through […]
Applications
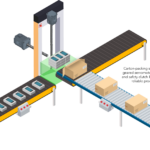
Packaging focus: Carton making and packing operations
Carton making and case packing are key operations in packaging facilities. Both rely on extremely fast motion systems with dozens of mechanically and programmatically linked axes for sufficient throughput to satisfy the demands of a global market. Case packing in particular is a common bottleneck. Typically, cartoners are installed at the ends of production lines, […]
Motion designs key to vertical farming
In a recent case study, we detailed how cable-systems manufacturer HELUKABEL helped automate a vertical-farming installation: Cables satisfy the unique demands of vertical farming. In contrast with approaches to optimize the traditional farming of fields, automated greenhouses solutions eliminate issues associated with tight labor markets, guarding delicate or valuable crops, and the need to apply […]
Floor rail system adds flexibility to assembly lines
LOSYCO, a specialist in rail-based intra-logistics and feeding systems, has provided five floor-level LOXrail floor rail system tracks for a German machine manufacturer’s two assembly lines. A newly developed transport solution allows the transport system to be adapted to three different track widths. A telescopic axis connects two customized carriers with a 1.5-ton payload, each […]
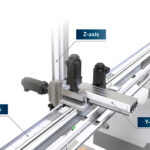
Simplifying overhead machine tending with long-travel automation
Cartesian robots with the right design upgrades can assume manual transfer operations. By Michael Everman • Founder and CTO | Bell-Everman Manufacturing and packaging operations using manual material or parts handling operations can reap immediate benefits from automation with long-travel Cartesian robots having custom end-of-arm tooling (EoAT) and advanced sensing capabilities. These robots can support […]
Advanced wafer transport automation improves precision and processing time
By Danielle Collins | Business Development Manager — Semiconductor • Bosch Rexroth With computer chip shortages affecting virtually every industry, semiconductor manufacturers are working rapidly to build new fabs and expand existing production lines. This increase in manufacturing capacity creates major opportunities — and challenges — for automation technology suppliers. Consider that the typical chip […]
Vesconite material gives rail-transport equipment decades of service
Actom Signalling, a Southern African railway signal-equipment company, has found minimal wear in accelerated wear testing on Vesconite slides in its point machines. These machines control railway tracks and switch the tracks to which particular trains will be directed. Actom engineering projects and contracts development technician Wayne Meyer confirms the test results. Testing was executed […]
LINAK lifting column takes cobot palletizers to new heights
There’s an untapped automation potential for palletizing goods in production and other industries. Realizing this potential requires flexible, easy-to-use, and affordable cobot solutions that can adjust to different palletizing setups and generate rapid return on investment. To meet these demands, LINAK now offers the ELEVATE lifting column — a new product that extends the reach […]
Comparing belt-drive types for automation applications
Synchronous belt drives dominate motion control designs for positioning and other precision functions. Here we detail V belts and other belt types used in industrial, robotic, and consumer designs for both linear and rotary axes. Modern flat belts are either endless (welded or otherwise closed into a hoop by the manufacturer) or open. Common on […]
Update on today’s belt drives
Belt drives have continued to evolve with new applications. Industrial belt drives in motion designs consist of rubber, engineered plastic, metal, or (most common) multi-material belts that wrap around drive pulleys — grooved or otherwise profiled wheels mounted on a shaft — in turn driven by electric motors. Powered by various motor types, belt drives run […]