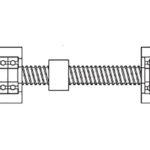
There are two instances when the terms “fixed bearing” and “floating bearing” are used in linear motion: to describe the support bearings used on ball and lead screws, and to describe linear guides mounted in parallel. And while the meanings of the terms are the same in both situations, their applications are different in each […]
Plastic + composite guides
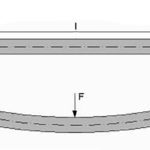
Mechanical properties of materials: stiffness and deflection
In a previous post, we looked at the stress-strain curve and its relationship to various aspects of material strength — tensile strength, yield strength, and fracture mechanics strength, for example. And while we often think of materials and structures in terms of strength, technically, “strength” is a measure of how much force a material can […]
What is curvilinear motion and when is it used?
In single-axis motion systems, travel is typically either linear (in a straight line) or rotary (in a partial or complete circle). But some applications call for a system that combines straight sections of motion with curved sections — referred to as curvilinear motion. Curvilinear systems generally take one of two forms: simple, constant-radii sections (such as […]
Linear motion trends in slides: Robotics and mobile designs lead the charge
Demand for simple-to-install and pre-integrated linear-slide systems continues unabated … especially in applications only recently automated. Here’s the perspective of Matt Mowry, North American market manager for drylin products at igus: “We’ve supplied fully assembled and customized linear-slide tables … complete with motors and accessories. We’ve also supplied custom-extruded linear profiles and bearing liners to […]
Selecting shafts for linear bearings: two things you need to know
In a round shaft linear bearing system, the shaft acts as the inner raceway of the bearing and plays a significant role in the wear and life of the system. Both recirculating and plain linear bearings as well as track-roller wheel-based linear bearings can use a wide variety of shaft materials, depending on the application […]
Beam deflection equations for linear systems
When a linear guide, such as a round shaft or profiled rail, deflects or sags, the bearings that travel along the guide experience edge loading (a higher load concentrated at the ends of the bearing), which can cause rough, irregular movement, increased wear, and reduced bearing life. And when a linear guide is incorporated into […]
What causes plain bearing wear?
For rolling element bearings, the L10 life calculation is an easy way to determine the bearing’s expected travel life. But for plain bearings, determining life expectancy is not so straightforward. Plain bearing life is based on the amount of wear the bearing experiences, which depends on factors that are unique to each application, such as […]
Can plain bearings be used for cantilevered loads?
There are few linear motion applications in which the load is perfectly centered over the supporting bearing. On the contrary – the majority of applications involve loads that are cantilevered, meaning they are offset from the bearing and induce a moment load. In this context, the term “bearing” can mean a single bearing or a […]
What limits linear bearing speed? (Part 2)
In part 1 of this series on bearing speed, we looked at the factors that limit the speed of linear recirculating bearings. In this segment, we’ll look at the factors that limit the speed of linear plain bearings. Linear plain bearings operate with sliding contact between the two bearing surfaces, so the limitations encountered with […]
Dissipating static electricity in urethane rollers and wheels
Static electricity is an invisible field of protons, neutrons, and electrons found in anything that has potential to move. Each atom has its own properties and characteristics. One of these properties is an electrical charge. Protons have what is called a “positive” (+) charge, which is the root of static electricity buildup in urethane […]