When designing and configuring an automated warehouse, one design goal is to keep the system as light and compact as possible. Depending on the size of the load being moved, there are two common types of automated warehouses. In lighter applications, aluminum structures can handle loads up to 100 kilograms, while steel structures are good for heavier loads of more than 100 kilograms.
Most traditional warehouses use forklifts with limited height, while automated warehouses make use of vertical space. Choosing the right components is key to making sure an automated warehousing system optimizes logistics management. And linear actuators are a good place to start.
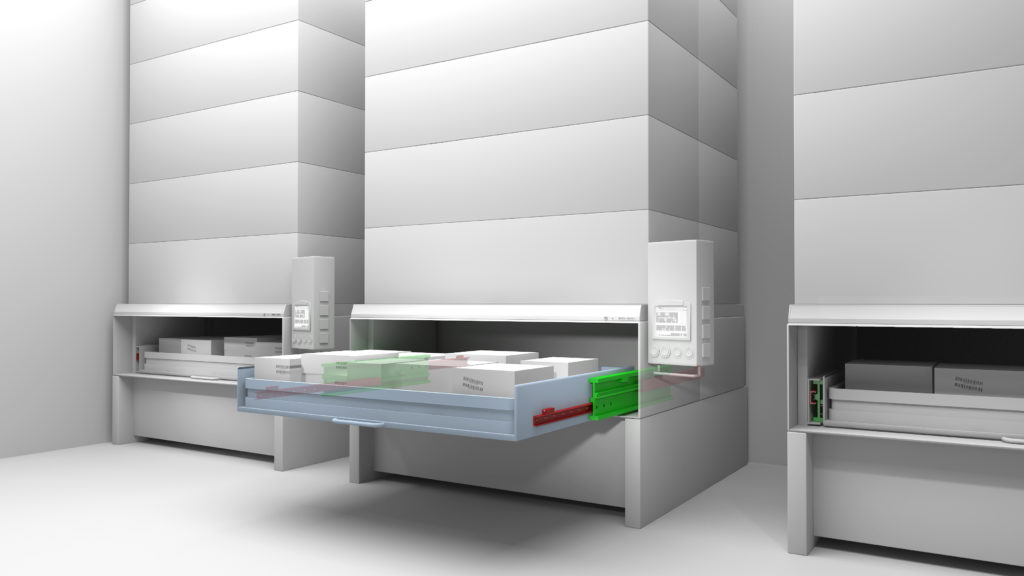
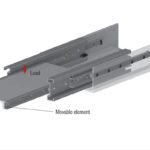
Often used for the picking arm in automated warehousing shuttles, the inductively hardened raceways of telescopic rails deliver optimal running properties. They exhibit little deflection when subjected to heavy loads, even when fully extended.
One recent critical handling application in the medical industry used linear actuators to give this automated warehouse a new look.
Pick and place system for test tubes
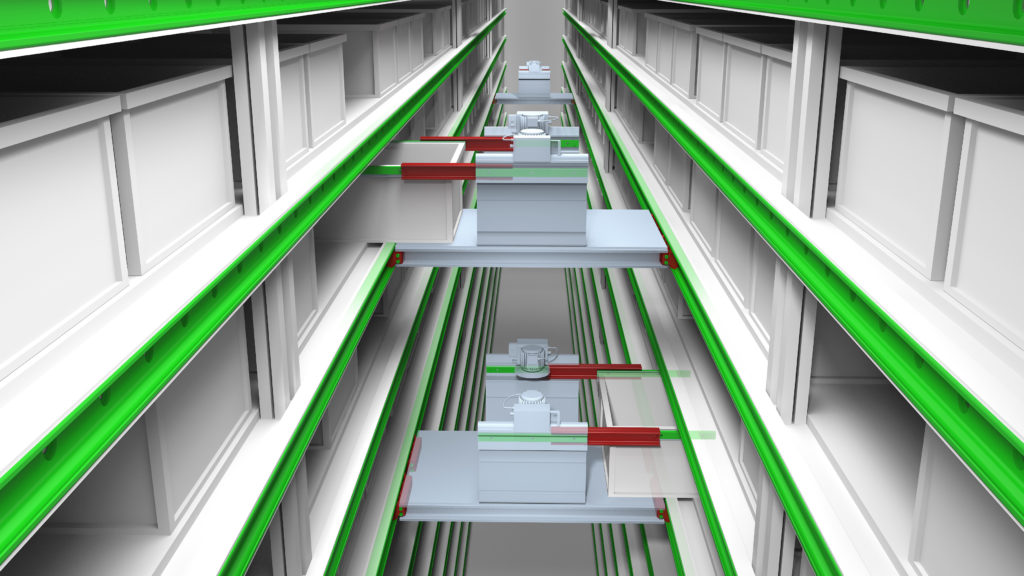
This pick-and-place system moves test tube containers for blood tests in a refrigerated warehouse. The robot moves along a network of axes to reach shelves positioned along the automated warehouse corridors, adopting a perpendicular trajectory and changing direction by 90 degrees. Further complicating the situation is the possibility of irregular surfaces where the rails slide.

As the robot passes from one track to a perpendicular track, this type of handling is managed with common recirculating ball bearings that need precise alignments. At the same time, configuring a sliding system with wheels or a set of bearings on the rails doesn’t guarantee the necessary stability and precision needed to place objects.
The task was to find the right solution for these handling operations and a reliable configuration for the entire system.
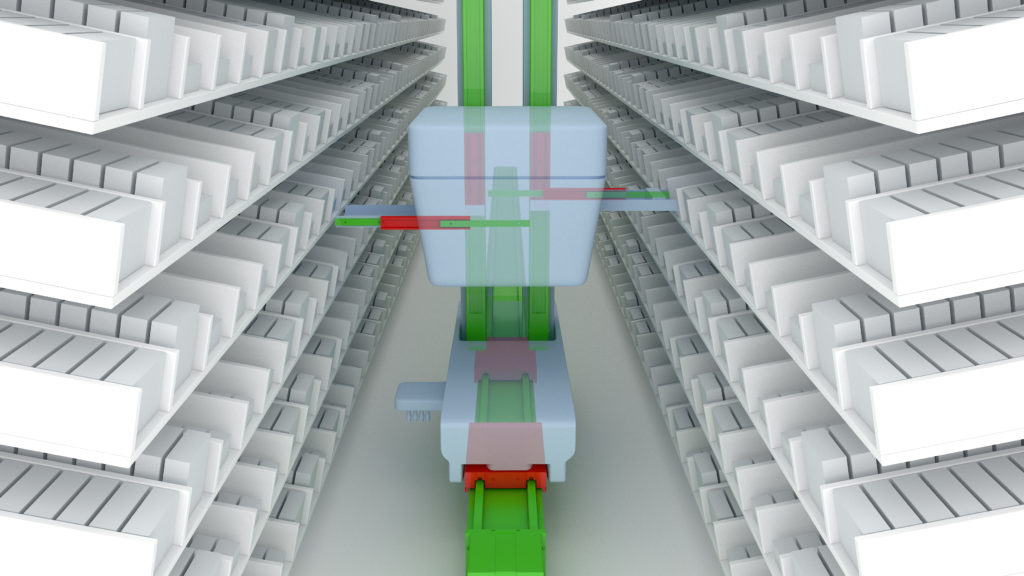
Precise, smooth robotic handling
Since the customer needed smooth, accurate movements along the X-axis, Rollon recommended its compact rail for managing the system’s robotic movements and helping it reach and pick up test tubes positioned on warehouse shelves. Available with different profiles and a slider that fits into a rail profile, these linear rails come with hardened raceways that absorb any surface misalignments.
Rollon managed the passage from the X- to Y-axis by mounting another pair of sliders on the carriage to sustain and move the robot, as well as two sections of rails positioned perpendicularly to the first set. When the carriage reaches the lateral position, it unhooks from the main axis, and two additional sliders enter the perpendicular rails and guide the robot along the Y-axis. The convenient size of the compact rail bearing helps manage the passage of sliders from the rail sections on the carriage, to the perpendicular rail tracks with relative ease. Made from hardened steel, this system consists of hardened raceways and high precision radial ball bearing sliders.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.