Gear sizes are typically specified by one of two designations:
Module or diametral pitch.
While both specifications define the size of the gear teeth, module and diametral pitch are calculated differently, with module (sometimes referred to as metric pitch) being the metric sizing standard and diametrical pitch being the Imperial (inch) sizing method.

Standard modules for straight and helical gears are defined by ISO 54:1996 and indicate the amount of pitch diameter (or pitch length, in the case of a straight rack) that each tooth occupies. The larger the module, the larger the gear teeth and the overall gear.
![]()
m = module (mm)
d = pitch diameter or pitch length (mm)
n = number of teeth
Module can also be found by dividing the circular pitch by pi (π).
![]()
m = module (mm)
p = circular pitch (mm)

Image credit: Kohara Gear Industry
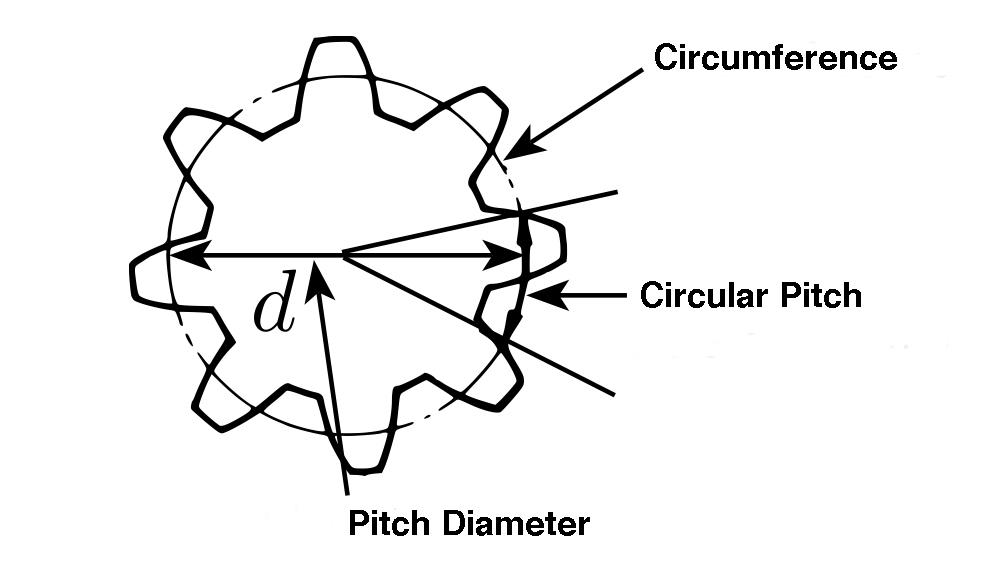
To find the circular pitch of a gear, divide the circumference around the pitch circle (circumference = pi x pitch diameter) by the number of teeth.
![]()
p = circular pitch (mm)
d = pitch diameter (mm)
n = number of teeth
By removing the circular constant of pi (π), the module system simplifies the calculations for other gear parameters.
Diametral pitch, on the other hand, indicates the number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter. It’s important to note that tooth (and, therefore, gear) size varies inversely with the diametral pitch. In other words, a larger diametral pitch means there are more — and, therefore, smaller — teeth per inch of pitch diameter.
![]()
DP = diametral pitch (1/in)
n = number of teeth
d = pitch diameter or pitch length (in)

Image credit: R. K. Mobley
Because it’s based on Imperial units, diametral pitch is used primarily in the U.S. However, most high-precision rack and pinion drives — both within and outside of the U.S. — use module size designations.
Module and diametral pitch are inverses of one another and are related by the millimeter-to-inch conversion of 25.4, where:
![]()
DP = diametral pitch (in)
m = module (mm)
Although module and diametral pitch are similar, mating gears with different sizing schemes can’t be used together or directly interchanged. In other words, mating gears must have either the same module (for example, m2 pinion with m2 rack) or the same diametral pitch (for example, 12DP pinion with 12DP rack).
Note that these calculations are for rack and pinion drives with spur (straight) teeth. For versions with helical teeth, there are two measures of pitch (normal and transverse), and therefore, two versions of module and two versions of diametral pitch.
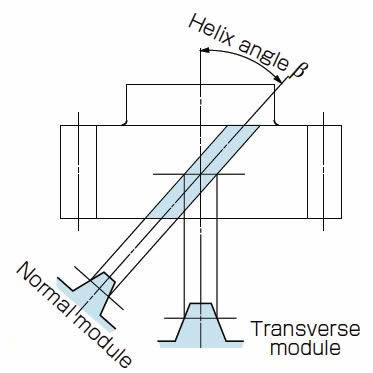
Image credit: QTC Metric Gears






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.