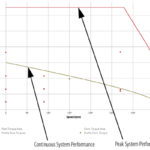
Servo motors are typically used for dynamic applications, where quick acceleration rates necessitate high torque production. In fact, one of the defining characteristics of a servo system is its ability to precisely control torque across a wide speed range, and the various speeds and torques required during the application’s move profile are a key parameter […]
Controls for linear axes
When should you use microstepping control for stepper motors?
Stepper motor operation is relatively straightforward. The drive sends pulses of current to the motor, and each pulse advances the motor by one step, or fraction of a revolution. The amount of movement per current pulse depends on the design of the stator and rotor. For permanent magnet stepper motors, a full step angle of […]
What is servo tuning and why is it important?
Unlike stepper motors, which rely on even pulses of current to turn the motor in discreet steps, servo motors operate with continuous current to reach a specified position, velocity, or torque. The precise amount of current to be delivered to the motor is determined by the servo controller, based on information supplied by an encoder […]
How does closed-loop stepper control work … and why not just use a servo?
Stepper motors are inherently open-loop devices. They don’t require feedback because each pulse of current delivered by the drive equals one step of the motor (or a fraction of a step in the case of microstepping). Plus with small step sizes (or step angles) the motor’s position can be determined very precisely without the need […]
New piezo driver with 1,200 W of power for fast switching applications
PI (Physik Instrumente) has released the new model E-619, a high-power piezo amplifier designed to drive high-capacitance multilayer piezo actuators with rapid rise times or high frequencies. As a special form of electro-ceramics, piezo materials are the gold standard when it comes to speed, force, and precision in a small package. Providing sink/source currents up […]
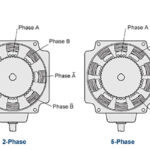
How does the number of stator phases affect stepper motor performance?
Stepper motors move in discrete steps when current is applied to coils in the stator. The size of the step is determined, in part, by the number of phases in the stator. In general, the more stator phases, the smaller the basic step angle and the higher the motor’s resolution. Stepper motors come in three basic types […]
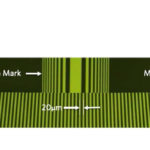
When is resolution important for linear systems?
Accuracy and repeatability are standard specifications that describe how a linear motion system behaves along its travel and how closely it reaches the intended position. Resolution, on the other hand, is less often included in performance data for linear motion systems, but it can be equally important as accuracy and repeatability in some applications. In […]
New wireless RF remote control for actuators from Accu Tech USA
Accu Tech USA has released a new wireless key fob controller for their linear actuator product line. The plug-and-play radio frequency (RF) remote control kit includes a 2-button remote control and a remote receiver to efficiently convert a standard rod-style actuator to an actuator automated by remote control. This system is small in size and […]
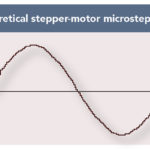
What is microstepping?
Microstepping is a method of controlling stepper motors, typically used to achieve higher resolution or smoother motion at low speeds. Stepper motors move in discrete steps, or fractions of a revolution. For example, a stepper motor with a 1.8 degree step angle will make 200 steps for every full revolution of the motor (360 ÷ […]
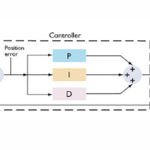
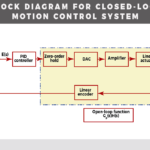
PID design using frequency-domain methods
With motion control applications, a PID or proportional + integral + derivative controller is often implemented using tuning or by a trial-and-error process on the shop floor. But modeling of the motion control system allows analytical derivation of the PID controller terms. By Tom Radigan | Advanced Motion Concepts Inc. Modeling a motion control system […]